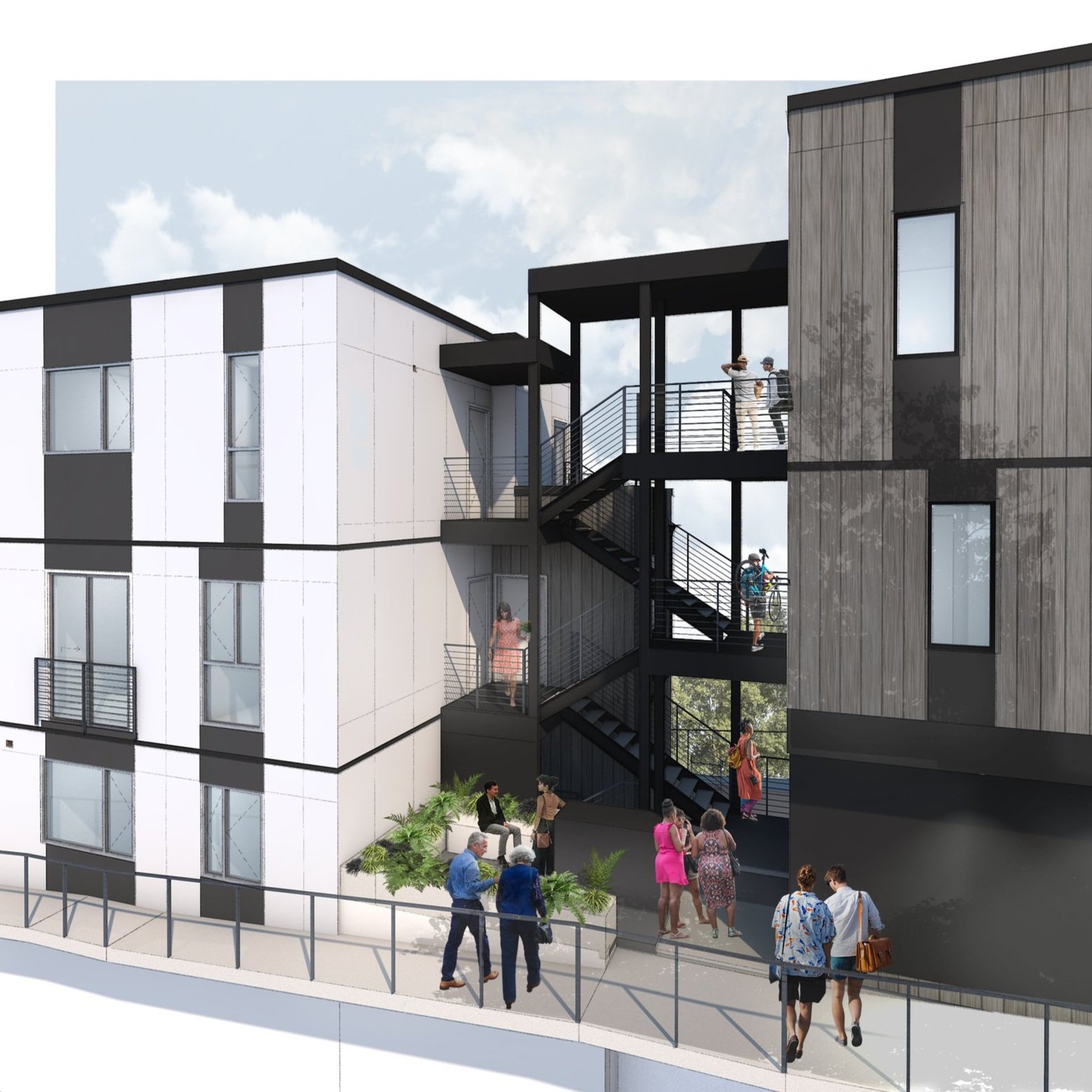
Completed in 2023 the 13th Avenue Apartments features one of b9 architects’ cleanest and simplest designs to date. Seeking our help in 2018, the client had already gone through an early design process with another architect, but the design they arrived at could not be realized due to code compliance issues. Through a flexible and collaborative design process, the team created an elegant, 20-unit infill project, mid-block on 13th Avenue in Seattle’s Capitol Hill neighborhood. With an elegant and organized facade that belies its complicated design, the 13th Avenue Apartment represents excellence that can be achieved with the right client, material selection and detailing.
When the project first came to b9 architects, it looked very different. With another firm’s preliminary Design Review proposal that did not have a path to meeting Seattle’s land use, energy or building codes, our design team worked with the client to propose a new solution. After an initial site investigation, the client agreed to have b9 restart the design process, keeping the idea of two structures, but connecting them with a series of stacked exterior walkways and interior stairwell and elevator. This strategy allowed the “front” structure to act as a centerpiece for the design while the structure in the rear could act as a secondary element. With an engaged client and multiple b9 team members owning specific aspects of the project, the design process focused on collaboration and quick decision making to move the project forward, helping the client make up for lost time.
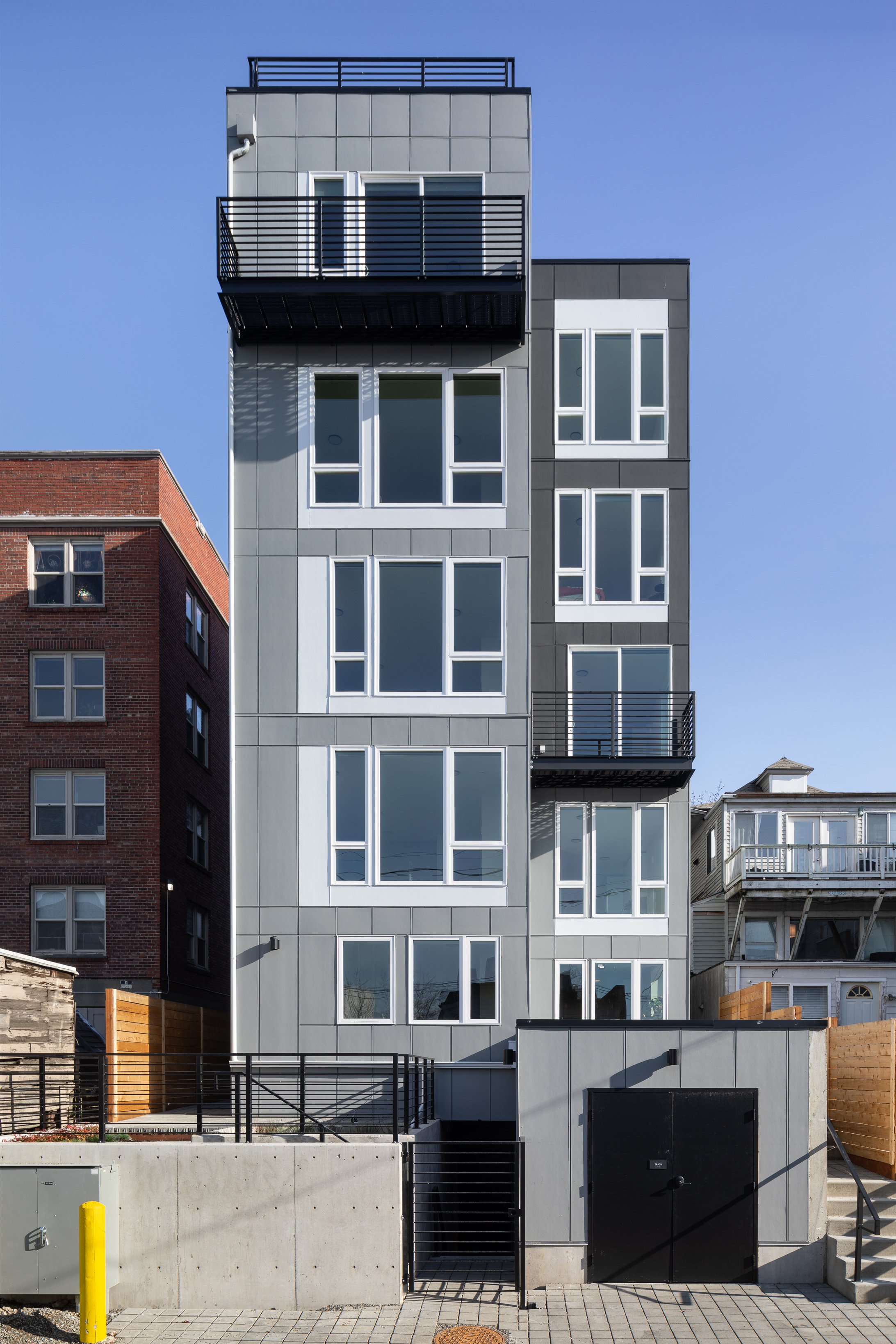
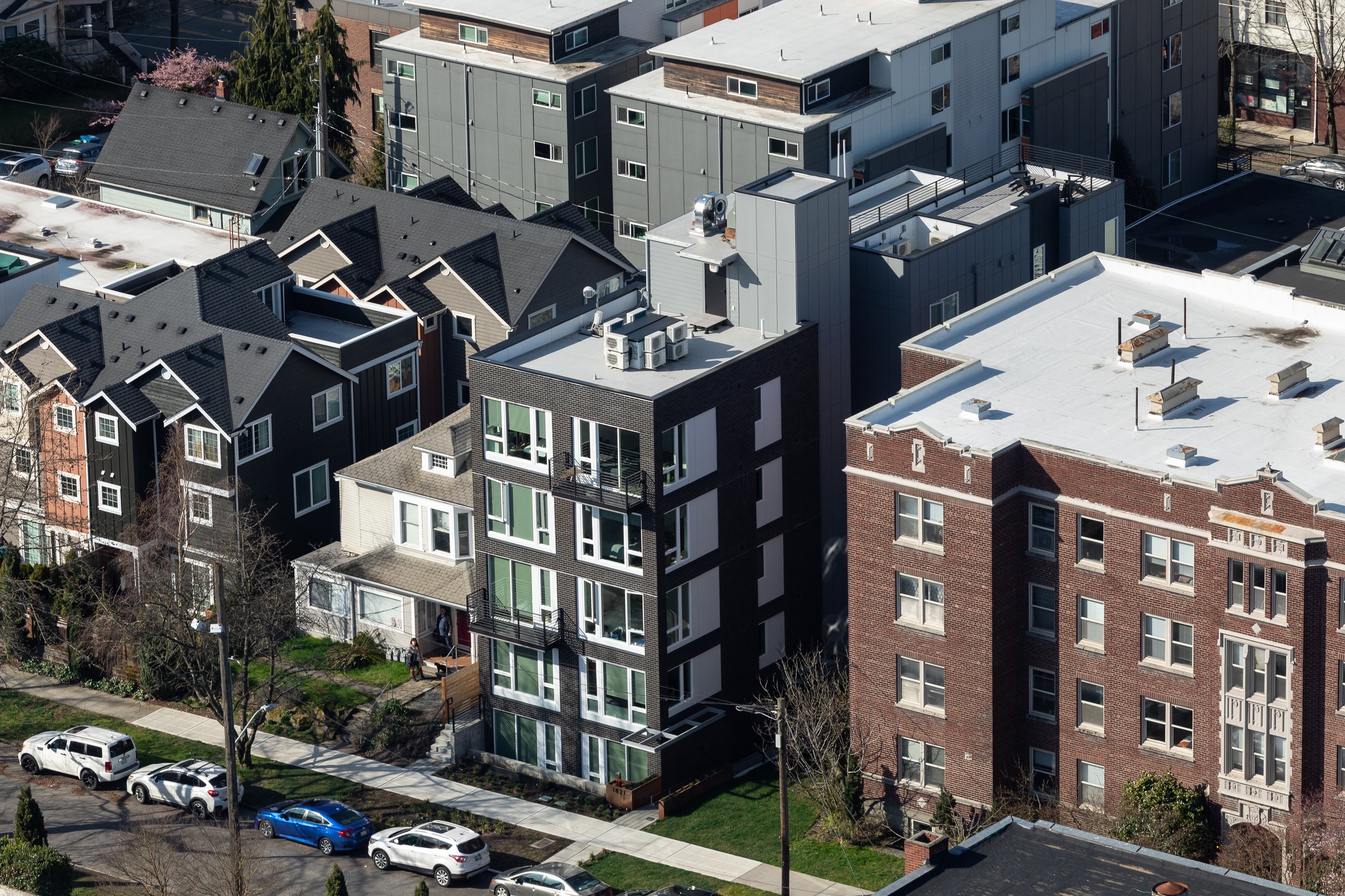
The project design takes advantage of the “single exit” allowance in the Seattle Building Code. Limited to 4 units per floor and a maximum distance between each unit’s entry and the stair and elevator, the project benefits from providing only one stair. The elevator permits the project to provide a small roof deck for all residents with access to amazing views of downtown Seattle, the Puget Sound and the Olympic Peninsula and Olympic Mountains beyond. The circulation spaces are the “connector” described above that tie the front and rear portions of the structure together. From the street, the building reads as two elements due to the circulation being inset from the north and south side facades. The rear facade shifts half of the mass to provide relief for the homes across the alley and to create a variety of unit types within the project.
Due to the dimensions of the site, the modulation at the center of the site creates relief to adjacent sites, similar to many of b9’s infill housing projects. However, the difference at this site is that the front facade is purposely clear and simple. The Design Review process in Seattle frequently encourages projects to undulate massing to create depth along street frontages. With a site at 35’ wide by 120’ feet deep, we were adamant that the front façade should be flat and create depth and texture primarily with material expression. There is no space for the front facade. Instead of shifting in or out, the 13th Avenue Apartments relies on simple detailing, a brick frame or grid complemented with contrasting infill panels and large windows and doors. As an assembled integral colored material, brick creates texture and depth on the front volume of the project. Limited to two projecting balconies, this is the simplest front facade b9 has designed. When taken as a whole, the project is complex, carving out the center of the site to setback from an adjacent Single Family home to the south and established brick apartment to the north.